Introduction to concrete building products
Practical Action
that a stronger and richer concrete is required than for conventional hollow blocks and quality
control needs to be very good. However, ventilation blocks can be sold at a premium price, so it can
be very worthwhile for producers to make them if they are confident that they can maintain the
required quality.
Producers need to follow national or international guidelines and guidelines for the sizes of blocks.
Typical sizes are 40 x 20 x 20 centimetres for hollow or solid blocks and 20 x 10 x 10 centimetres
for bricks for the length, width and height.
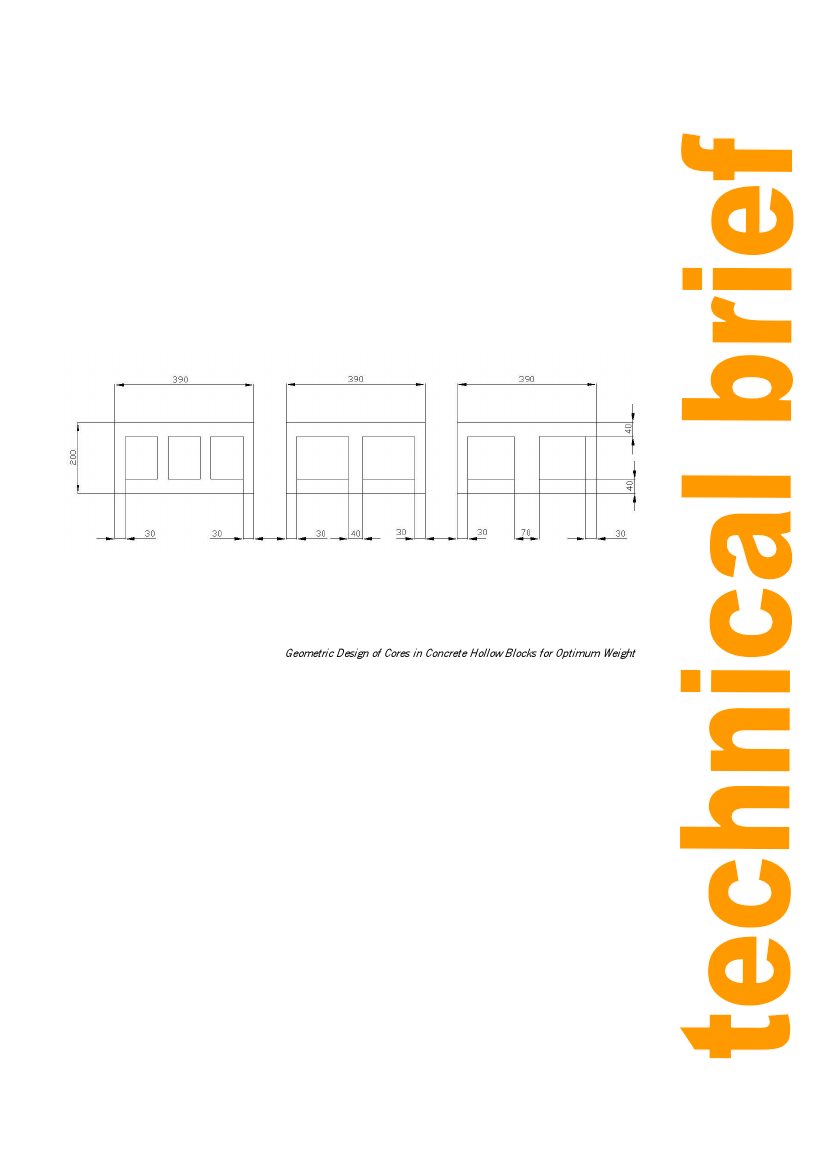
The following are some typical dimensions for hollow blocks, showing the hollow sections. Most
blocks are made with two or three cavities. Larger numbers of cavities are possible, but this makes
the mould design and the moulding process more complicated. More than three cavities may be
used, for example, if steel reinforcing rods are to be pushed through the blocks then grouted in to
give concrete block structures that are strong in tension and bending as well as in compression.
Block with three
cavities
Block with two cavities
Two cavity block
strengthened for structural
use.
Figure 1: Dimensions of Concrete Blocks Showing Cavities, in millimetres.
Illustration: Neil Noble / Practical Action. From Geometric Design of Cores in Concrete Hollow Blocks for Optimum Weight,
by Fada Casi Al-Subaei, Master of Science Thesis, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia, 1994.
Curved concrete blocks, usually solid, can also be made, for example for circular buildings or water
tanks. With more elaborate moulds straight or curved concrete blocks can also be made
interlocking in which an extended section from one block slots into a groove of the next block. In
this way buildings made with interlocking blocks can be strengthened. However, the sizes of
interlocking blocks need to conform to very tight specifications as otherwise there are gaps between
the fitting of successive blocks and the building structure does not work as well.
Tiles and Slabs
These products are thin and rectangular and most commonly comprise:
• Roofing tiles
• Wall tiles
• Floor tiles
• Paving slabs
• Fencing panels
• Pit latrine slabs.
Paving can also carried out with pavers, which resemble more closely small concrete bricks than
slabs. Pavers are more commonly used for highly active areas, especially where there is vehicular
traffic as they are far less likely to crack and break in service.
Concrete roofing, wall and floor tiles are usually made with just sand and cement and no coarse
aggregate such as gravel or crushed rock. This is because of their thinness, usually 6 to 20mm in
height, although floor tiles may be thicker. Such a mix can be called micro-concrete (mc).
5